Python接口自动化测试的学习笔记7接口关联

Python接口自动化测试的学习笔记7——接口关联
1、引言
在接口自动化测试领域,接口间的关联是非常重要的一环。当某个接口的响应数据被下游接口作为输入参数时,我们就需要在测试过程中实现接口之间的数据关联。本文将深入探讨如何在Python接口自动化测试中实现接口关联。
2、问题背景
在实际的业务场景中,常见的接口关联形式如登录接口返回的token用于后续接口的身份验证,或者是列表接口返回的数据ID用于详情接口的查询等。因此,在编写自动化测试脚本时,我们必须妥善处理这些关联数据,确保测试的连贯性和准确性。
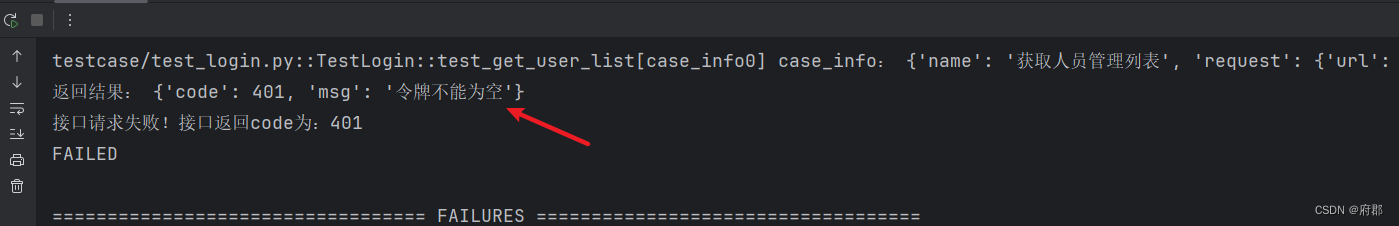
例如,我想请求这个接口,那么在请求时必须要带token才能请求正常,那么问题来了,我们要怎么去拿到token呢?

不带token请求时
3、解决方法
一般在请求登录接口时,接口返回结果中有token参数,我们只要把这个token提取并储存起来拿给后面的接口调用就行,下面就简单来介绍两种方法来实现接口关联。
介绍之前大家可以看下获取人员接口的代码和测试数据
py文件
@pytest.mark.parametrize('case_info', YamlUtil().read_testcases_yaml('get_user_list.yml'))
def test_get_user_list(self, case_info):
print('case_info:', case_info)
url = case_info['request']['url']
method = case_info['request']['method']
headers = case_info['request']['headers']
print('headers:', headers)
data = case_info['request']['data']
# requests.request请求
res = RequestsUtil().send_request(url=url, method=method, headers=headers, data=data)
# 获取返回结果数据,json格式接收
response = res.json()
# 打印返回结果到控制台
print('返回结果:', response)
# 获取接口返回code
res_code = response['code']
assert res_code == 200, print(f"接口请求失败!接口返回code为:{res_code}")yaml文件
- name: 获取人员管理列表
request:
url: 'http://xxx/system/user/getList'
method: post
headers:
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization:
data:
nickName:
groupId:
roleId:
PageNumber: 1
PageSize: 10
validate: Null方法1:使用全局变量存储调用
可以在class类下添加access_token变量,默认给空值,然后通过提取登录接口返回的access_token进行赋值
class TestLogin:
access_token = None
@pytest.mark.parametrize('case_info', YamlUtil().read_testcases_yaml('login.yml'))
def test_login(self, case_info):
print('case_info:', case_info)
url = case_info['request']['url']
method = case_info['request']['method']
data = case_info['request']['json']
# requests.request请求
res = RequestsUtil().send_request(url=url, method=method, json=data)
# 获取返回结果数据,json格式接收
response = res.json()
# 打印返回结果到控制台
print('返回结果:', response)
# 获取接口返回code
res_code = response['code']
if res_code == 200:
TestLogin.access_token = response['data']['access_token']
print('access_token:', TestLogin.access_token)
else:
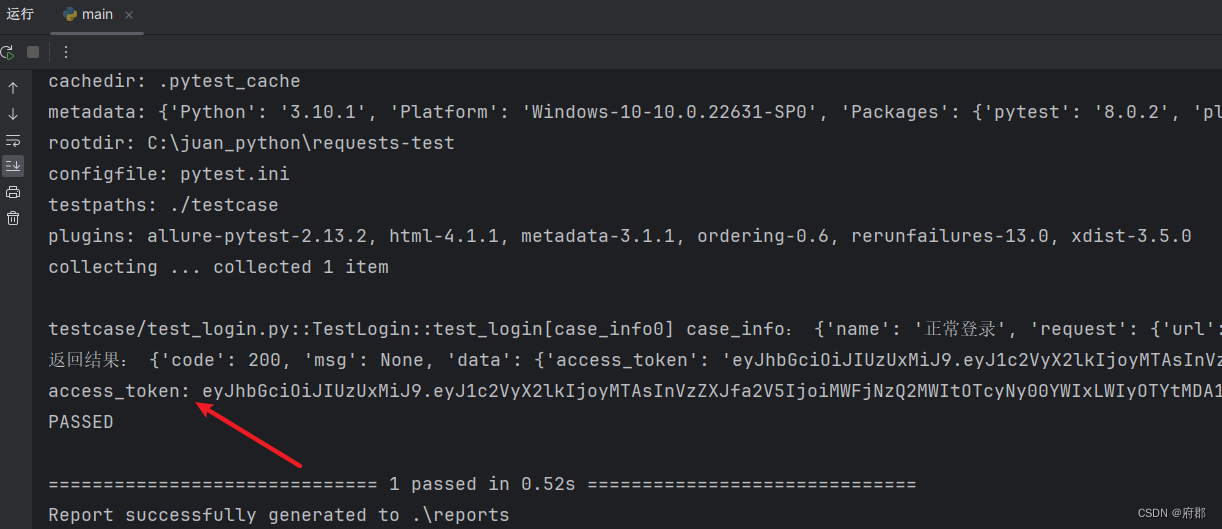
print(f"接口请求失败!接口返回code为:{res_code}")查看执行结果,我们可以看到token已经成功提取到了
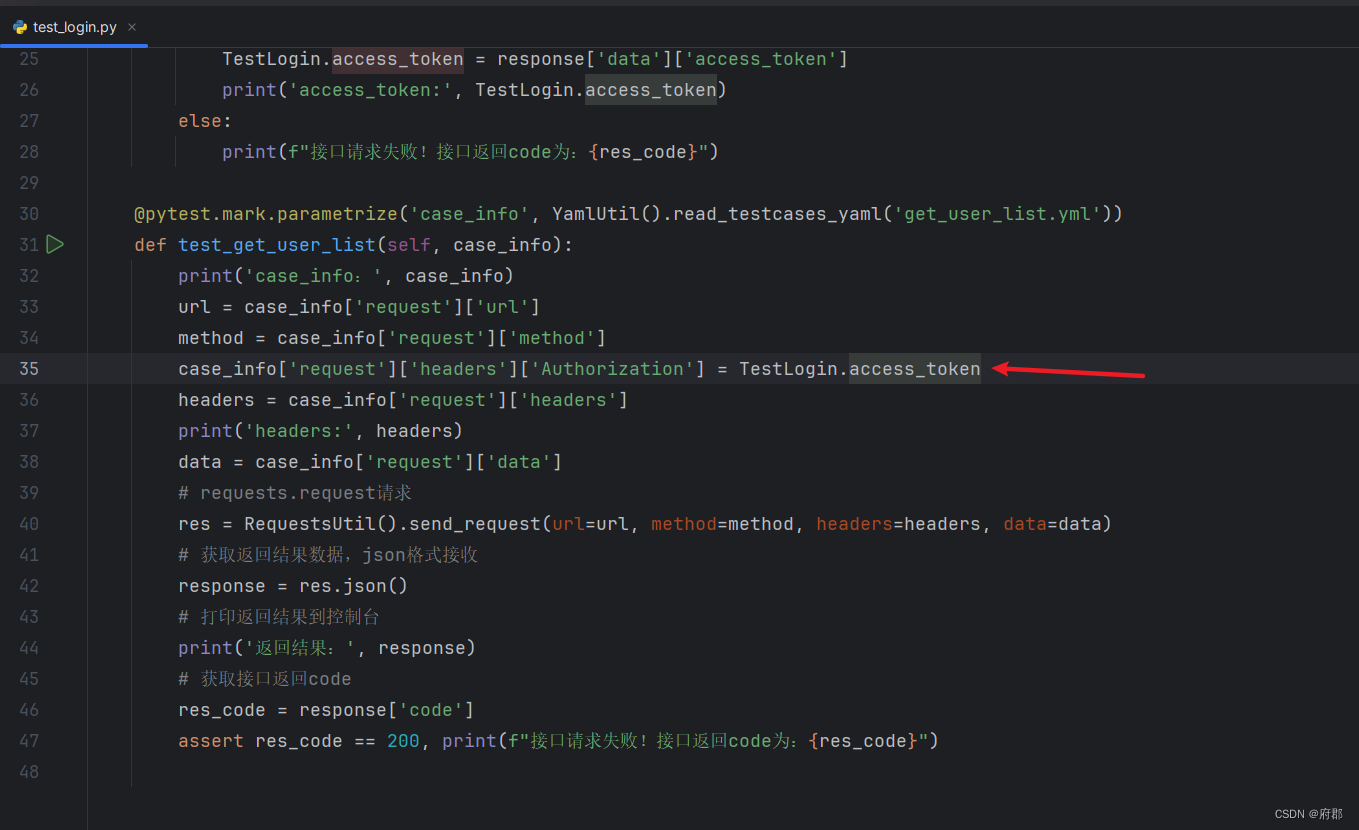
下面我们只要在获取人员接口把这个参数加进去就行了
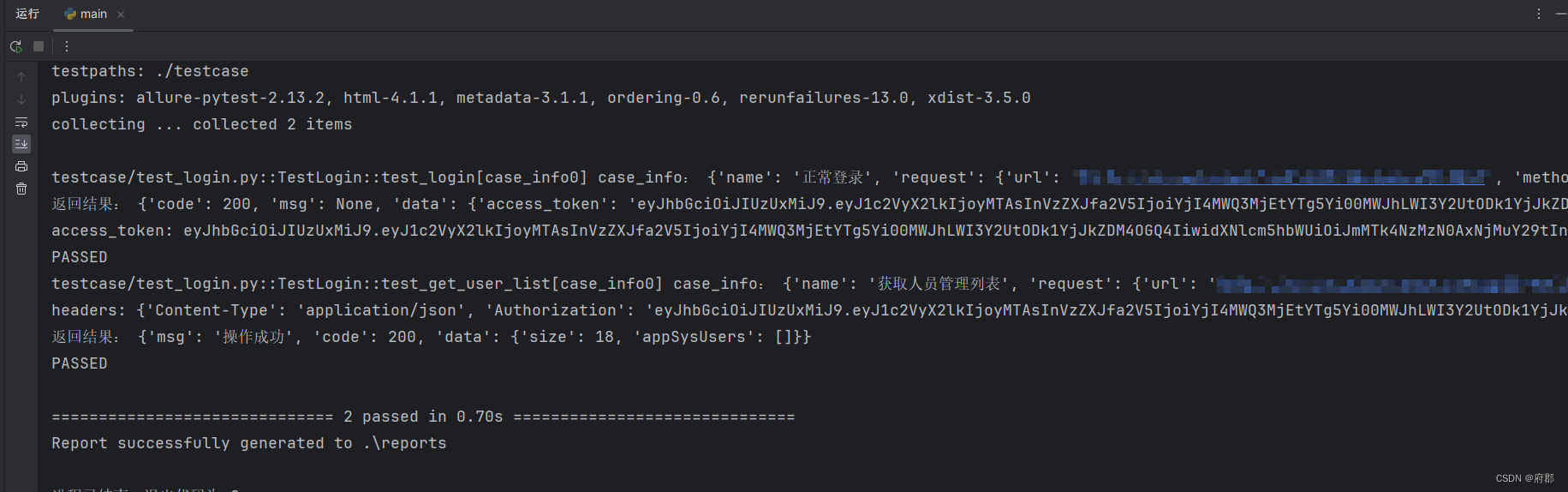
查看执行结果,两个用例都执行通过了,说明这样操作是可行的。
方法2 (推荐) :使用YAML文件存储接口关联数据
然而,在实际的接口自动化测试或项目开发中,通常不建议直接使用全局变量来存储敏感信息如token。因为这样会使得token在程序运行期间始终存在于内存中,增加了安全风险,并且不利于代码维护和测试复用。更好的做法是将token存储在配置文件(如YAML、INI等)或者环境变量中,并在需要的时候从这些持久化存储中读取。
例如我们可以将token存储到YAML文件中,那么我们要怎么做呢?
1)首先,在根目录下新建一个extract.yml文件,用来存储token和其他接口关联需要用到的参数,文件名可自定义,再在yaml_util.py文件中封装下extract.yml文件的读写方法
# 读取extract.yml文件
def read_extract_yaml(self, key):
with open(os.getcwd() + "./extract.yml", mode='r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
value = yaml.load(stream=f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
try:
if key in value.keys():
return value[key]
except Exception as e:
print(f"key值{e}不存在")
# 追加插入数据到extract.yml文件
def insert_extract_yaml(self, data):
with open(os.getcwd() + "./extract.yml", mode='a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
yaml.dump(data=data, stream=f, allow_unicode=True)2)然后,在登录接口中我们使用jsonpath来提取token,提取完后,将数据以字典格式存储到extract.yml文件中
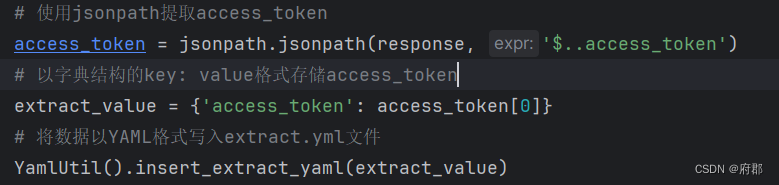
查看执行结果
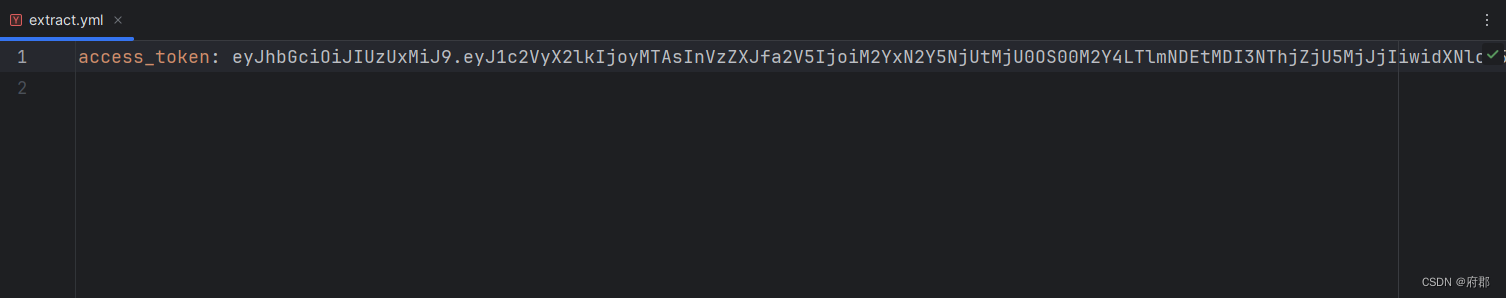
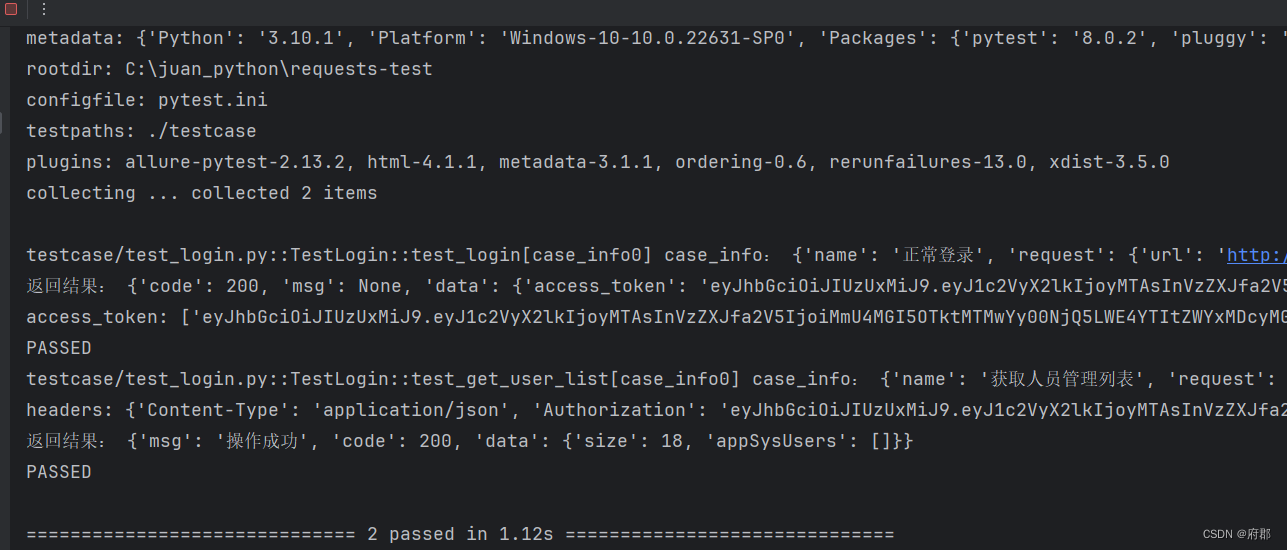
3)最后,在获取人员接口处调用读取extract.yml文件函数

查看最终执行结果
完整代码:
import jsonpath
import pytest
from config.requests_util import RequestsUtil
from common.yaml_util import YamlUtil
class TestLogin:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('case_info', YamlUtil().read_testcases_yaml('login.yml'))
def test_login(self, case_info):
print('case_info:', case_info)
url = case_info['request']['url']
method = case_info['request']['method']
data = case_info['request']['json']
# requests.request请求
res = RequestsUtil().send_request(url=url, method=method, json=data)
# 获取返回结果数据,json格式接收
response = res.json()
# 打印返回结果到控制台
print('返回结果:', response)
# 获取接口返回code
res_code = response['code']
if res_code == 200:
# 使用jsonpath提取access_token
access_token = jsonpath.jsonpath(response, '$..access_token')
# 以字典结构的key: value格式存储access_token
extract_value = {'access_token': access_token[0]}
# 将数据以YAML格式写入extract.yml文件
YamlUtil().insert_extract_yaml(extract_value)
print('access_token:', access_token)
else:
print(f"接口请求失败!接口返回code为:{res_code}")
@pytest.mark.parametrize('case_info', YamlUtil().read_testcases_yaml('get_user_list.yml'))
def test_get_user_list(self, case_info):
print('case_info:', case_info)
url = case_info['request']['url']
method = case_info['request']['method']
case_info['request']['headers']['Authorization'] = YamlUtil().read_extract_yaml('access_token')
headers = case_info['request']['headers']
print('headers:', headers)
data = case_info['request']['data']
# requests.request请求
res = RequestsUtil().send_request(url=url, method=method, headers=headers, data=data)
# 获取返回结果数据,json格式接收
response = res.json()
# 打印返回结果到控制台
print('返回结果:', response)
# 获取接口返回code
res_code = response['code']
assert res_code == 200, print(f"接口请求失败!接口返回code为:{res_code}")注意:这里每次执行登录接口后都会多增加一条token进来,所以我们需要在每次执行用例之前清除下extract.yml文件的数据,以保证所需数据为最新的。

4、总结
接口关联是接口自动化测试的重要组成部分,通过Python及其相关库,我们可以灵活有效地处理各种接口间的关联逻辑,从而实现高效准确的接口自动化测试。在实际工作中,关注接口间的业务关联,编写合理的测试脚本,是保证接口测试质量、提升测试效率的关键所在。