Vue框架和前后端开发VueBase

目录
Vue框架和前后端开发【VueBase】
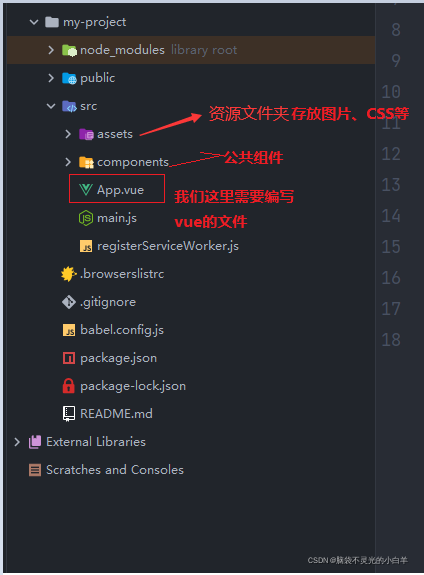
Vue环境搭建与创建项目
构建Vue的开发环境
相关环境
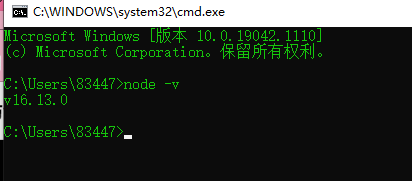
Node: 【根据需要进行下载】
安装完成后
node -v测试安装是否成功
npm 镜像 cnpm:
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.orgwebpack: 构建工具
开发工具:vsCode:
高亮现实:扩展 -> 搜索:Vetur
搭建Vue环境
也可以直接参考 进行搭建
- 安装 vuecli 工具
cnpm install -g @vue/cli
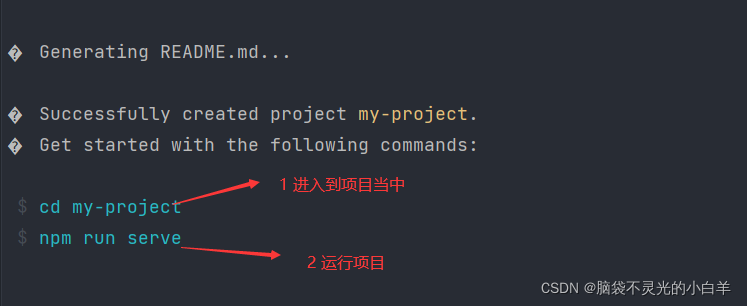
vue create my-project
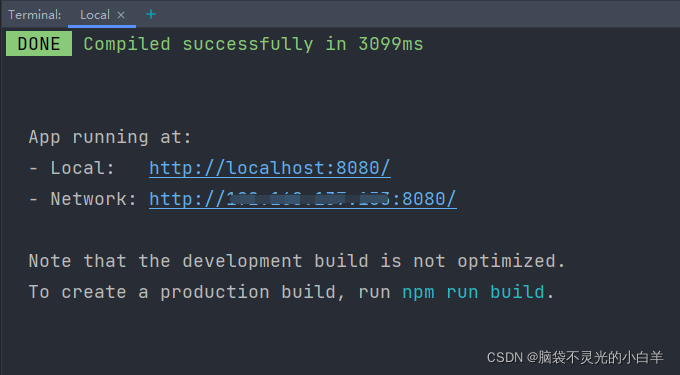
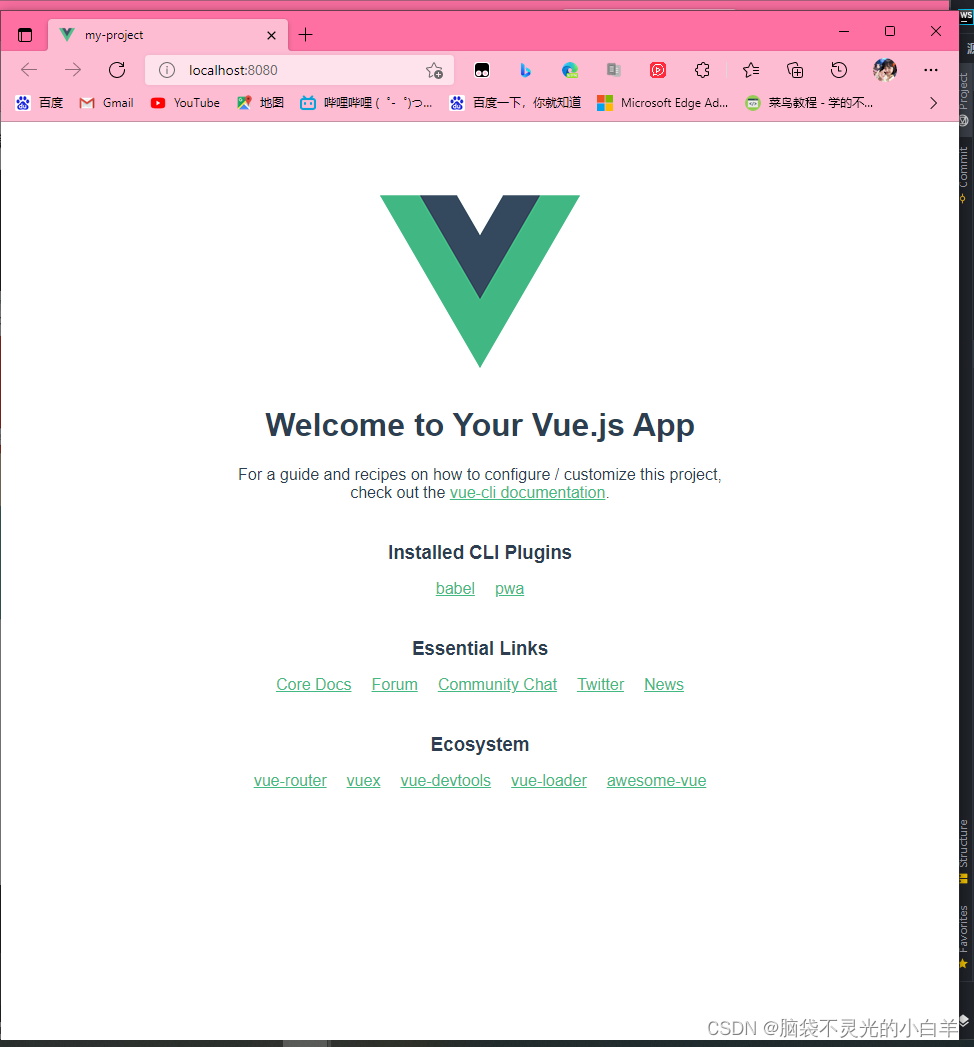
npm run serve创建vue项目的时候选择手动创建
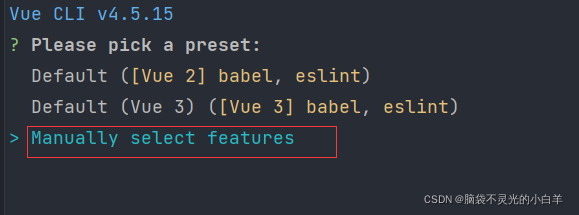
通过
空格
进行选择,【目前学习阶段选择以下即可】
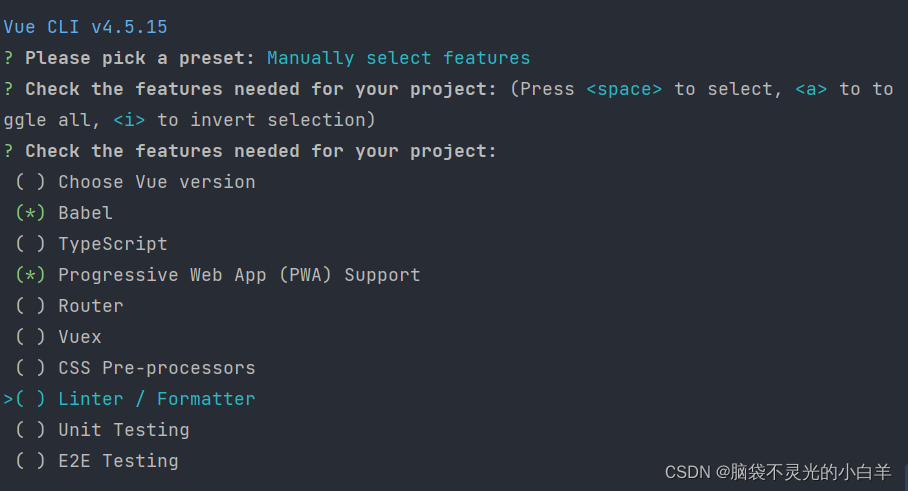

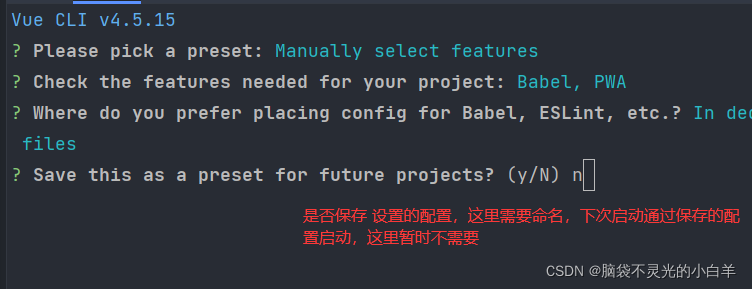
接下来就是开始创建需要的资源和依赖了
Vue的基础知识
学习流程
1. 模版语法
1. 插值
1. 文本: {{ }}
2. 原始HTML: v-html
3. 属性: v-bind:attr [动态的绑定属性]
4. 模版语法使用限制: 每个绑定都只能包含单个表达式
2. 指令
3. 缩写
1. v-bind:可以直接缩写成 :<!-- 1. 文本: {{ }} -->
<template>
<div id="app">
<h3>模板语法</h3>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg: "这是一个模板语法"
}
},
components: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>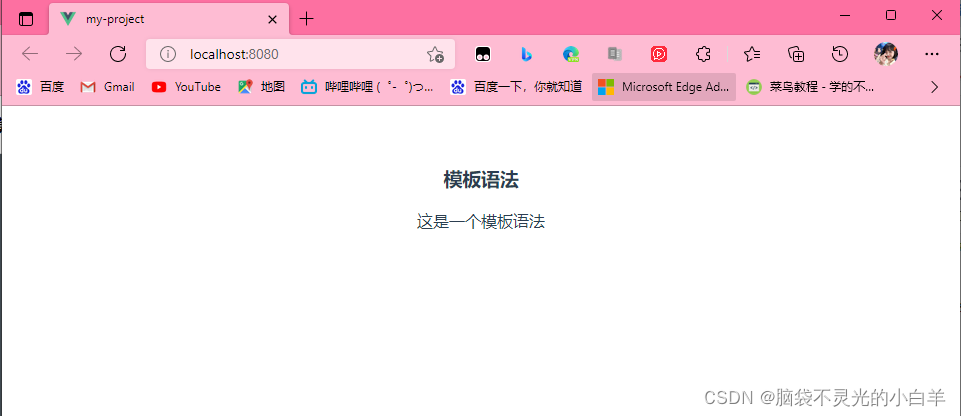
<!-- 2. 原始HTML: v-html -->
<template>
<div id="app">
<h3>模板语法</h3>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
<!-- <p>{{price}}</p>-->
<div v-html="price"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg: "这是一个模板语法",
price:"<h3>300</h3>"
}
},
components: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>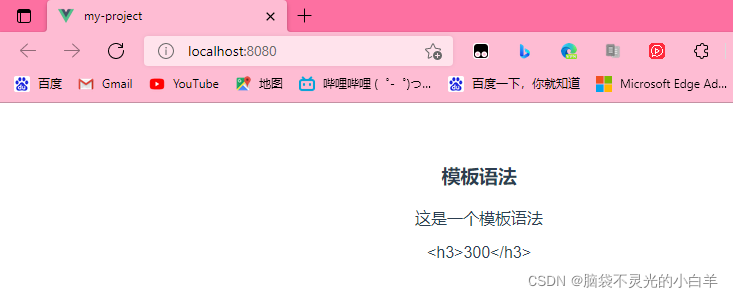
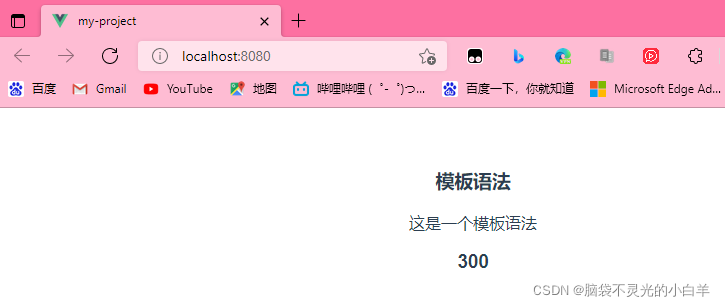
3. 属性: v-bind:attr [动态的绑定属性]
<template>
<div id="app">
<h3>模板语法</h3>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
<!-- <p>{{price}}</p>-->
<div v-html="price"></div>
<div v-bind:class="active">hello</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg: "这是一个模板语法",
price:"<h3>300</h3>",
active:"active"
}
},
components: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style><!-- 4. 模版语法使用限制: 每个绑定都只能包含单个表达式-->
<template>
<div id="app">
<h3>模板语法</h3>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
<!-- <p>{{price}}</p>-->
<div v-html="price"></div>
<div v-bind:class="active">hello</div>
<div>{{ number + 1 }}</div>
<div>{{ ok ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}</div>
<div>{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg: "这是一个模板语法",
price:"<h3>300</h3>",
active:"active",
number:1,
message: "hello world"
}
},
components: {
}
}
</script>2. 条件渲染
1. v-if
2. v-else
3. template
4. v-show<template>
<div id="app">
<h3>模板语法</h3>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
<!-- <p>{{price}}</p>-->
<div v-html="price"></div>
<div v-bind:class="active">hello</div>
<div>{{ number + 1 }}</div>
<div>{{ ok ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}</div>
<div>{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}</div>
<div>
<h3>条件渲染</h3>
<p v-if="flag">孙悟空</p>
<p v-else>六耳猕猴</p>
<!--v-if 基于元素的移除和添加 -->
<template v-if="flag">
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
</template>
<!-- v-show 基于元素的显示与隐藏 -->
<div v-show="flag">hello show</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg: "这是一个模板语法",
price:"<h3>300</h3>",
active:"active",
number:1,
message: "hello world",
flag:true
}
},
components: {
}
}
</script>3. 列表渲染
1. v-for
2. 数组的更新检测<template>
<div id="app">
<div>
<h3>列表渲染</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in result" :key="index">{{ item.text }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg: "这是一个模板语法",
price:"<h3>300</h3>",
active:"active",
number:1,
message: "hello world",
flag:true,
result: [
{
id: 1001,
text: "东京的水",
},
{
id: 1002,
text: "印度的疫情",
},
{
id: 1003,
text: "中国的特斯拉",
}
]
}
},
components: {
}
}
</script>4. 事件处理
1. v-on:click
2. methods:承载事件函数
3. v-on: 可以直接缩写成 @
4. 事件传递参数
5. 修饰符 <div>
<h3>事件处理</h3>
<p v-if="flags">我是新人,请多关照</p>
<button @click="clickHandle">按钮</button>
<ul>
<li
@click.stop="getMessageHandle(item.text, $event)"
v-for="(item, index) in result"
:key="index"
>
{{ item.text }}
</li>
</ul>
<a @click.prevent="clickIwenHandle" href="http://iwenwiki.com">iwen</a>
</div>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg: "这是一个模板语法",
price:"<h3>300</h3>",
active:"active",
number:1,
message: "hello world",
flag:true,
result: [
{
id: 1001,
text: "东京的水",
},
{
id: 1002,
text: "印度的疫情",
},
{
id: 1003,
text: "中国的特斯拉",
}
],
flags: false,
};
},
methods: {
clickHandle() {
this.flags = !this.flags;
},
getMessageHandle(data, e) {
console.log(data, e);
},
clickIwenHandle() {
console.log(1111);
},
addItemHandle() {
// this.result.push({
// id:1004,
// text:"加油加油"
// })
this.result = this.result.concat([{ id: 1004, text: "加油加油" }]);
},
clickInputHandle() {
console.log(this.username);
},
getMessages() {
return this.message.split("").reverse().join("");
},
getHelloMessageHandle(data){
console.log(data);
this.helloMessage = data;
}
},
components: {
}
}
</script>5. 表单输入与绑定
1. v-model
2. 修饰符
.lazy 【懒惰的,不会实时获取】
.number 【只能输入数字】
.trim 【去掉前后空格】 <div>
<h3>表单的输入与绑定</h3>
<p>{{ username }}</p>
<input type="text" v-model.lazy="username" />
<button @click="clickInputHandle">获取</button>
</div>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg: "这是一个模板语法",
price:"<h3>300</h3>",
active:"active",
number:1,
message: "hello world",
flag:true,
result: [
{
id: 1001,
text: "东京的水",
},
{
id: 1002,
text: "印度的疫情",
},
{
id: 1003,
text: "中国的特斯拉",
}
],
flags: false,
};
},
methods: {
clickHandle() {
this.flags = !this.flags;
},
getMessageHandle(data, e) {
console.log(data, e);
},
clickIwenHandle() {
console.log(1111);
},
addItemHandle() {
// this.result.push({
// id:1004,
// text:"加油加油"
// })
this.result = this.result.concat([{ id: 1004, text: "加油加油" }]);
},
clickInputHandle() {
console.log(this.username);
},
},
components: {
}
}
</script>6. 计算属性vs侦听器
1. computed
2. watch <div>
<h3>计算属性vs侦听器</h3>
<p>{{ message.split("").reverse().join("") }}</p>
<p>{{ getMessage }}</p>
<p>{{ getMessages() }}</p>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="nick">
</div>
</div>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
data() {
return {
helloMessage:"",
nick:"",
message: "Hello",
username: "",
msg: "这是一个模版语法",
price: "<h3>300</h3>",
active: "active",
count: 0,
flag: false,
result: [
{
id: 1001,
text: "东京的水",
},
{
id: 1002,
text: "印度的疫情",
},
{
id: 1003,
text: "中国的特斯拉",
},
],
flags: false,
};
},
methods: {
clickHandle() {
this.flags = !this.flags;
},
getMessageHandle(data, e) {
console.log(data, e);
},
clickIwenHandle() {
console.log(1111);
},
addItemHandle() {
// this.result.push({
// id:1004,
// text:"加油加油"
// })
this.result = this.result.concat([{ id: 1004, text: "加油加油" }]);
},
clickInputHandle() {
console.log(this.username);
},
getMessages() {
return this.message.split("").reverse().join("");
},
},
computed: {
getMessage() {
return this.message.split("").reverse().join("");
},
},
components: {
},
};
</script>7. Class 与 Style 绑定
1. 数组
2. 对象 <div>
<h3>Class 与 Style 绑定</h3>
<p :class="{ 'active':true }">hello class</p>
<p :class="['a1','a2']">Hello Class2</p>
<p :class="[{'active':true},'a1','a2']">Hello Class3</p>
</div>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
data() {
return {
helloMessage:"",
nick:"",
message: "Hello",
username: "",
msg: "这是一个模版语法",
price: "<h3>300</h3>",
active: "active",
count: 0,
flag: false,
result: [
{
id: 1001,
text: "东京的水",
},
{
id: 1002,
text: "印度的疫情",
},
{
id: 1003,
text: "中国的特斯拉",
},
],
flags: false,
};
},
methods: {
clickHandle() {
this.flags = !this.flags;
},
getMessageHandle(data, e) {
console.log(data, e);
},
clickIwenHandle() {
console.log(1111);
},
addItemHandle() {
// this.result.push({
// id:1004,
// text:"加油加油"
// })
this.result = this.result.concat([{ id: 1004, text: "加油加油" }]);
},
clickInputHandle() {
console.log(this.username);
},
getMessages() {
return this.message.split("").reverse().join("");
},
getHelloMessageHandle(data){
console.log(data);
this.helloMessage = data;
}
},
computed: {
getMessage() {
return this.message.split("").reverse().join("");
}
},
watch:{
nick(newValue,oldValue){
console.log(newValue,oldValue);
}
},
components: {
},
};
</script>组件基础
1. 创建组件
(1)在components 中创建一个 .vue文件
(2)输入 vue 回车生成组件基本模板
2. 引用组件
(1)在App.vue 里面可以通过在
<script>
// 引入
import Hello from "./components/Hello"
export default{
components:{
Hello,//注入
},
};
</script>方式引入组件
直接通过标签的形式使用组件,例如:<Hello />
3. 组件是独立实例化,data必须是一个函数
4. props: 父传子 [重点]
5. 自定义事件: 子传父Hello.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- 唯一根元素 -->
<p>组件:{{ title }}-{{ num }}</p>
<div>
<p>{{ count }}</p>
<button @click="count +=1 ">按钮</button>
</div>
<button @click="sendMessageHandle">传递数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
count:0,
message:"我是Hello的数据"
}
},
props:{
title:{
type:String,
default:"默认数据"
},
num:{
type:Number,
default:0
}
},
methods:{
sendMessageHandle(){
this.$emit("onMyEvent",this.message)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ helloMessage }}</p>
<Hello title="组件基础" :num="0" @onMyEvent="getHelloMessageHandle"/>
<Hello title="组件深入" />
<Hello />
<div>
<h3>模版语法</h3>
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
<div v-html="price"></div>
<div :class="active">hello</div>
<p>{{ count * 2 }}</p>
</div>
<div>
<h3>条件渲染</h3>
<p v-if="flag">孙悟空</p>
<p v-else>六耳猕猴</p>
<template v-if="flag">
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
</template>
<div v-show="flag">hello show</div>
</div>
<div>
<h3>列表渲染</h3>
<button @click="addItemHandle">添加数据</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in result" :key="index">{{ item.text }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<h3>事件处理</h3>
<p v-if="flags">我是新人,请多关照</p>
<button @click="clickHandle">按钮</button>
<ul>
<li
@click.stop="getMessageHandle(item.text, $event)"
v-for="(item, index) in result"
:key="index"
>
{{ item.text }}
</li>
</ul>
<a @click.prevent="clickIwenHandle" href="http://iwenwiki.com">iwen</a>
</div>
<div>
<h3>表单的输入与绑定</h3>
<p>{{ username }}</p>
<input type="text" v-model.lazy="username" />
<button @click="clickInputHandle">获取</button>
</div>
<div>
<h3>计算属性vs侦听器</h3>
<p>{{ message.split("").reverse().join("") }}</p>
<p>{{ getMessage }}</p>
<p>{{ getMessages() }}</p>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="nick">
</div>
</div>
<div>
<h3>Class 与 Style 绑定</h3>
<p :class="{ 'active':true }">hello class</p>
<p :class="['a1','a2']">Hello Class2</p>
<p :class="[{'active':true},'a1','a2']">Hello Class3</p>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Hello from "./components/Hello"
export default {
name: "App",
data() {
return {
helloMessage:"",
nick:"",
message: "Hello",
username: "",
msg: "这是一个模版语法",
price: "<h3>300</h3>",
active: "active",
count: 0,
flag: false,
result: [
{
id: 1001,
text: "东京的水",
},
{
id: 1002,
text: "印度的疫情",
},
{
id: 1003,
text: "中国的特斯拉",
},
],
flags: false,
};
},
methods: {
clickHandle() {
this.flags = !this.flags;
},
getMessageHandle(data, e) {
console.log(data, e);
},
clickIwenHandle() {
console.log(1111);
},
addItemHandle() {
// this.result.push({
// id:1004,
// text:"加油加油"
// })
this.result = this.result.concat([{ id: 1004, text: "加油加油" }]);
},
clickInputHandle() {
console.log(this.username);
},
getMessages() {
return this.message.split("").reverse().join("");
},
getHelloMessageHandle(data){
console.log(data);
this.helloMessage = data;
}
},
computed: {
getMessage() {
return this.message.split("").reverse().join("");
}
},
watch:{
nick(newValue,oldValue){
console.log(newValue,oldValue);
}
},
components: {
Hello, // 注入
},
};
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>Vue组件
1. 插槽
1. 插槽内容: <slot>
2. 编译作用域
3. 后备内容
4. 具名插槽
5. 作用域插槽2. 动态组件 & 异步组件
1. 动态组件
2. 异步组件
MyComponent.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>插槽</h3>
<div>
<slot name="header">默认值/缺省值</slot>
<hr>
<div>我是分割线</div>
<slot name='body'>默认值/缺省值</slot>
<hr>
<slot name="footer">默认值/缺省值</slot>
<slot :demo="demo"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
demo:"我是demo"
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<MyComponent>
<template v-slot:header>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
</template>
<template v-slot:body>
<div>我是内容部分</div>
</template>
<template v-slot:footer>
<div>我是底部</div>
</template>
<template v-slot:default="slotProps">
<h3>{{ slotProps.demo }}</h3>
</template>
</MyComponent>
<DyComponent />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyComponent from "./components/MyComponent"
import DyComponent from "./components/DyComponent"
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg:"我是头部!"
}
},
components: {
MyComponent,
DyComponent
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>Child1.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>Child1</h3>
<p>{{ $root.hello() }}</p>
<p>{{ $parent.msg }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
</style>Child2.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>Child2</h3>
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
<button @click="clickHandle">修改</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
msg:"第一次呈现数据"
}
},
methods:{
clickHandle(){
this.msg = "Hello2"
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>DyComponent.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>我是动态组件</h3>
<button @click="changeViewHandle">切换视图现实</button>
<keep-alive>
<component :is="currentComponent"></component>
</keep-alive>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child1 from "./Child1"
// import Child2 from "./Child2"
//异步组件
const Child2 = () => import ("./Child2");
export default {
data(){
return{
currentComponent:Child1,
msg:"我是Component"
}
},
components:{
Child1,
Child2
},
methods:{
changeViewHandle(){
if(this.currentComponent === Child1){
this.currentComponent = Child2
}else{
this.currentComponent = Child1
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>