rabbitmq-amqp事务消息消费失败重试机制prefetch限流

rabbitmq-amqp事务消息+消费失败重试机制+prefetch限流
1 安装和配置
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-amqp
com.fasterxml.jackson.core jackson-databind
1.2 yml 配置
生产端的配置
spring: rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 virtual-host: / # 虚拟主机 username: guest password: guest publisher-returns: true #确认消息已经发送到队列,生产上无需开启
simple:同步等待confirm结果,直到超时
#开启消息确认 :correlated:异步回调,MQ返回结果时会回调这个ComfirmCallback publisher-confirm-type: correlated #确认消息已发送到交换机
生产端的配置
spring: rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 virtual-host: / # 虚拟主机 username: guest password: guest publisher-returns: true #确认消息已经发送到队列,生产上无需开启
simple:同步等待confirm结果,直到超时
#开启消息确认 :correlated:异步回调,MQ返回结果时会回调这个ComfirmCallback publisher-confirm-type: correlated #确认消息已发送到交换机
2.生产端的消息确认发送代码
/**
- (1) RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback 这个接口是用来确定消息是否到达交换器的
- (2) RabbitTemplate.ReturnsCallback 这个则是用来确定消息是否到达队列的,未到达队列时会被调用 / @Service @Slf4j public class RabbitMqConfirmCallback implements RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback,RabbitTemplate.ReturnsCallback{ private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; public void queueConfirm(Map map) { // 第一个参数表示交换机,第二个参数表示 routing key,第三个参数即消息 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(“confirm_exchange”, “confirm_key1”, map, new CorrelationData(“111”)); // 故意输入一个不存在的交换机 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(“confirm_exchange_2222”, “confirm_key1”, map, new CorrelationData(“22222”)); // 故意输入一个不存在的队列 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(“confirm_exchange”, “confirm_key1_333333”, map, new CorrelationData(“3333”)); log.info(“Confirm – 消息–发送结束”); } /*
- 需要给ConfirmCallback赋值 不然不会走回调方法,默认是null
- //将当前类的实例设置为 RabbitMQ 的确认回调处理器,跟下面的confirm方法联合使用,
- // 还需要打开配置:spring: rabbitmq: publisher-confirm-type: correlated / @PostConstruct public void init(){ rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(this); rabbitTemplate.setReturnsCallback(this); } @Autowired public RabbitMqConfirmCallback(RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate) { this.rabbitTemplate = rabbitTemplate; // rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(this); } /* 此方法用于监听消息是否发送到交换机
- 回调 */ @Override public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) { if (ack) { log.info(“confirm – 监听消息成功发送到交换机–回调id = {}”, correlationData); } else { log.info(“confirm – 消息没有发送到交换机回调id= {},消息发送失败:{}。”, correlationData, cause); } } @Override public void returnedMessage(ReturnedMessage returnedMessage) { log.info(“消息未到达队列 — returnedMessage= " + returnedMessage); } }
2.2 生产端的截图
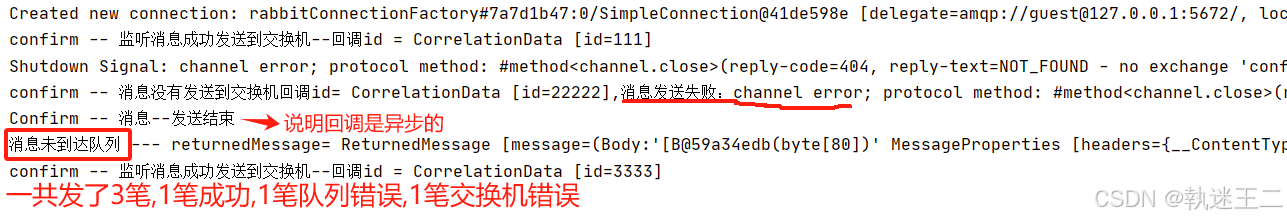
3.消费端代码
@Component @Slf4j public class RabbitConfirmConsumer { // 交换机 public static final String confirm_exchange_name = “confirm_exchange”; // 队列 public static final String confirm_queue_name=“confirm_queue”; // routingkey public static final String confirm_routing_key = “confirm_key1”; // 声明交换机 @Bean(“confirmExchange”) public DirectExchange confirmExchange(){ return new DirectExchange(confirm_exchange_name); } // 声明队列 @Bean(“confirmQueue”) public Queue confirmQueue() { return QueueBuilder.durable(confirm_queue_name).build(); } // 绑定队列到交换机 @Bean public Binding queueBingExchange(Queue confirmQueue,DirectExchange confirmExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(confirmQueue).to(confirmExchange).with(confirm_routing_key); } /**
- ack:成功处理消息,RabbitMQ从队列中删除该消息
- nack:消息处理失败,RabbitMQ需要再次投递消息
- reject:消息处理失败并拒绝该消息,RabbitMQ从队列中删除该消息 */ @RabbitListener(queues = “confirm_queue”) public void consumerConfirm(Message message, Channel channel, @Payload Map map, @Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long tag) throws IOException { //获取消息的唯一标记 long deliveryTag = message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(); log.info(“接收的消息为:{},消息的唯一标记={}, 直接注入的tag= {}",message, deliveryTag, tag); if(message.getBody() != null){ //获取消息的内容 byte[] body = message.getBody(); //basicAck:表示成功确认,使用此回执方法后,消息会被rabbitmq broker 删除。 channel.basicAck(deliveryTag,false);//false 表示仅确认当前消息消费成功 log.info(“接收的消息为:{}”, map); }else{ channel.basicReject(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),true); log.info(“未消费数据”); } } }
3.2消费端截图
 4
4
消费端重试机制 @Service @Slf4j public class RabbitRetryConsumer { @Bean public Queue retryQueue(){ Map params = new HashMap<>(); return QueueBuilder.durable(“retry_queue”).withArguments(params).build(); } @Bean public TopicExchange retryTopicExchange(){ return new TopicExchange(“retry_exchange”,true,false); } //队列与交换机进行绑定 @Bean public Binding BindingRetryQueueAndRetryTopicExchange(Queue retryQueue, TopicExchange retryTopicExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(retryQueue).to(retryTopicExchange).with(“retry_key”); } int count = 0; //测试重试,需要在yml配置 retry @RabbitListener(queues = “retry_queue”) public void retryConsumer(Map map, Channel channel, @Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long tag) throws Exception { log.info(“retryConsumer 重试次数 = {},重试接收数据为:{}",count++, map); int i = 10 /0; channel.basicAck(tag,false); } }
4.2 重试机制截图

5 限流设置–消费端
spring: rabbitmq: listener: simple: acknowledge-mode: manual # 开启手动确认模式 prefetch: 5 #控制消费者从队列中预取(prefetch)消息的数量,以此来实现流控制
5.1 生产端–发送19条信息
@GetMapping("/xianliu”) public String xianliuTest(){ for(int i = 1; i < 20; i++){ Map map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(“key”,“限流测试–” + i); rabbitMqProducer.xianliuTest(map); } return “限流测试发送成功”; } /***
- 限流消息的发送测试 */ public void xianliuTest(Map map) { // 第一个参数表示交换机,第二个参数表示 routing key,第三个参数即消息 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(“confirm_exchange”, “confirm_key1”, map, new CorrelationData(“111”)); }
5.2 消费端
/**
- ack:成功处理消息,RabbitMQ从队列中删除该消息
- nack:消息处理失败,RabbitMQ需要再次投递消息
- reject:消息处理失败并拒绝该消息,RabbitMQ从队列中删除该消息 */ @RabbitListener(queues = “confirm_queue”) public void consumerConfirm(Message message, Channel channel, @Payload Map map, @Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long tag) throws IOException { //获取消息的唯一标记 long deliveryTag = message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(); log.info(“接收的消息为:{},消息的唯一标记={}, 直接注入的tag= {}",message, deliveryTag, tag); if(message.getBody() != null){ //basicAck:表示成功确认,使用此回执方法后,消息会被rabbitmq broker 删除。 //channel.basicAck(deliveryTag,false);//false 表示仅确认当前消息消费成功 log.info(“接收的消息为:{}”, map); }else{ //否定确认 //channel.basicNack(deliverTag,false,true);//requeue为false,则变成死信队列 channel.basicReject(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),true); log.info(“未消费数据”); } }
5.3 注释掉channel.basicAck–堵塞了
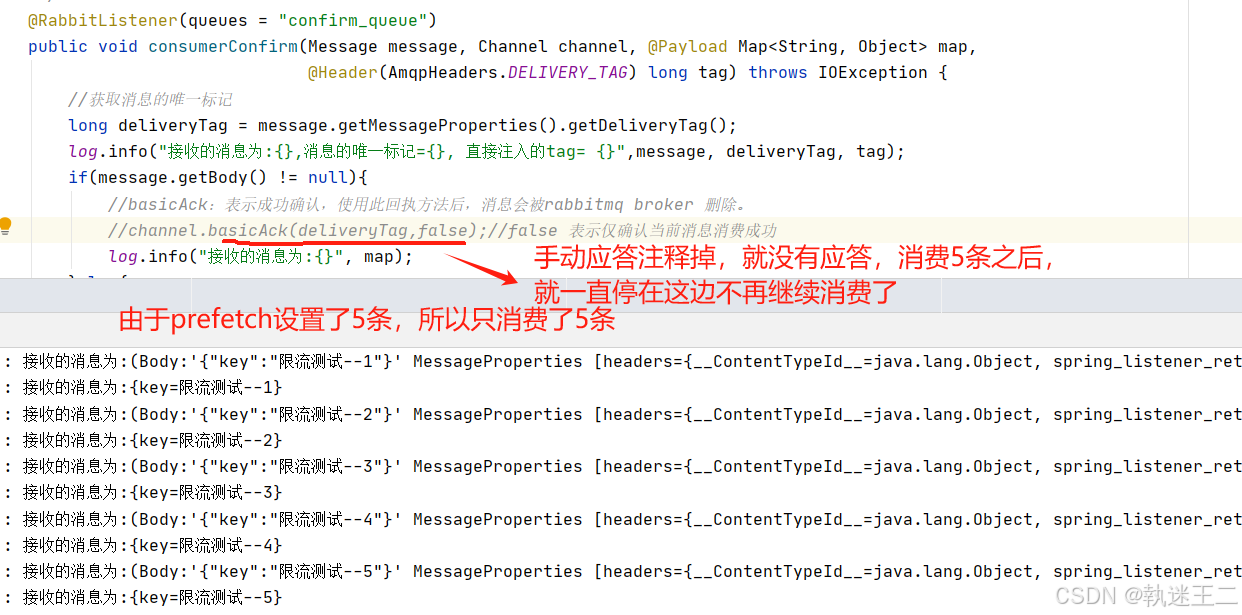
5.4 注释掉了 prefetch – 19条全部被消费,即使没有ack
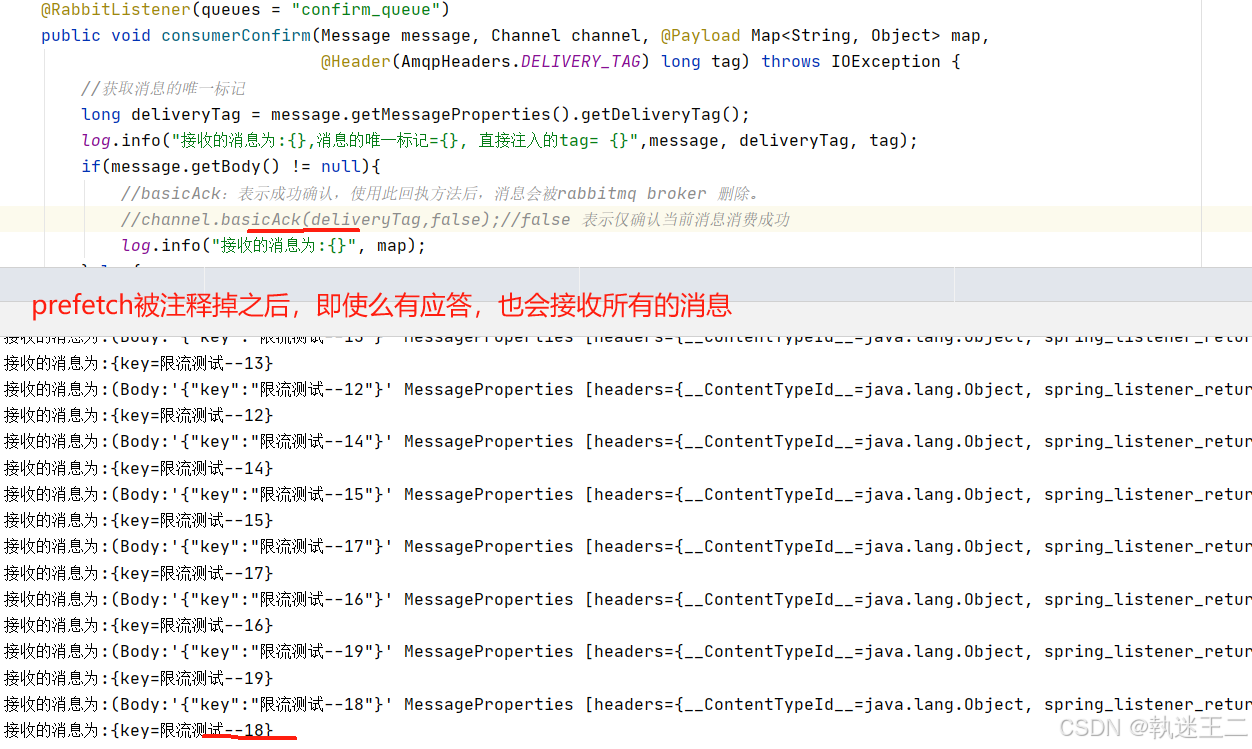
 4
4