3.9代码随想录第十二天打卡

目录
3.9代码随想录第十二天打卡
226.翻转二叉树 (优先掌握递归)
(1)题目描述:
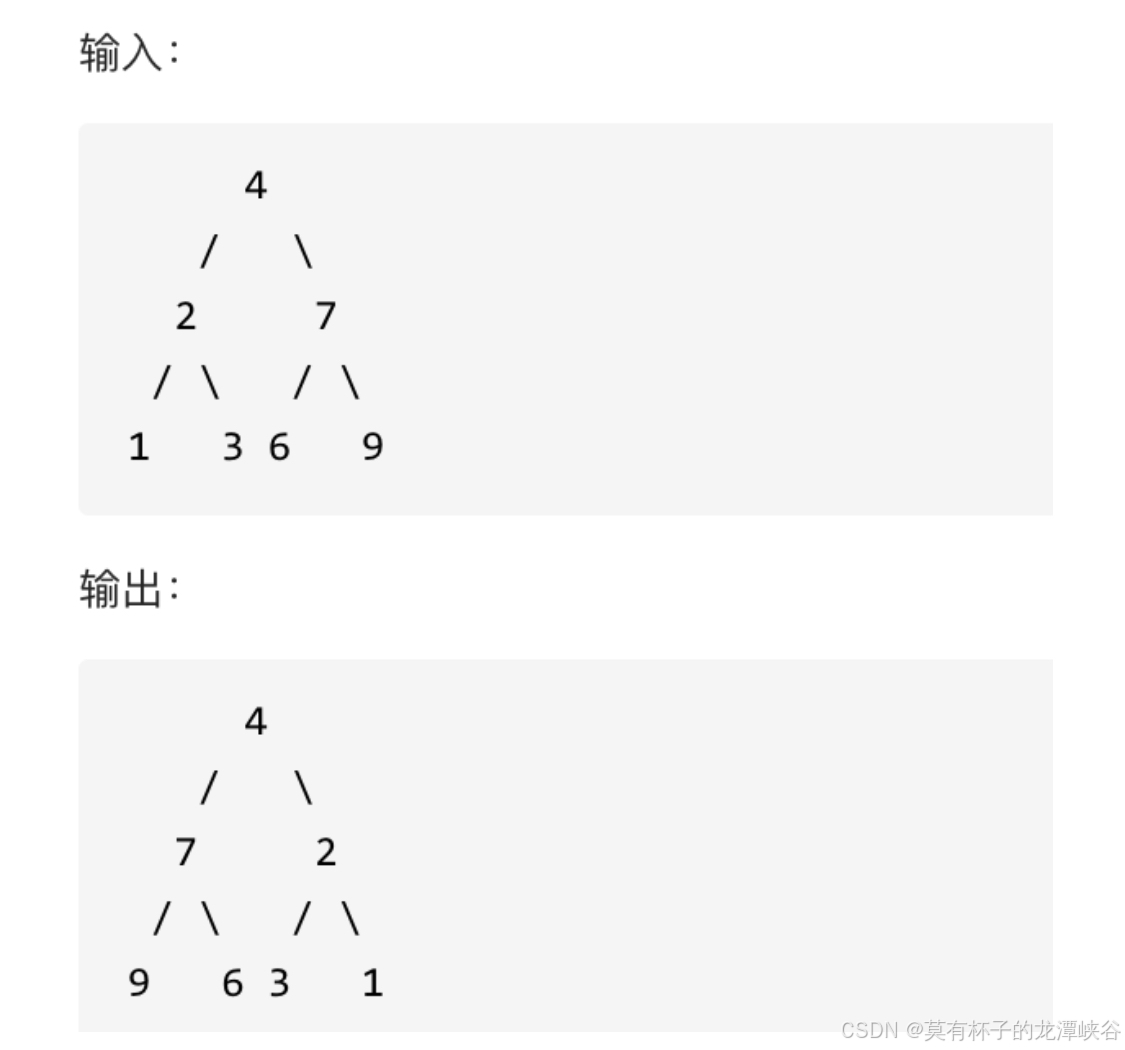
(2)解题思路:
1.递归方法的前序遍历
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return root;
swap(root->left, root->right); // 中
invertTree(root->left); // 左
invertTree(root->right); // 右
return root;
}
};2.后序遍历
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return root;
invertTree(root->left); // 左
invertTree(root->right); // 右
swap(root->left, root->right); // 中
return root;
}
};3.中序遍历(区别是要一直处理左子树)
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return root;
invertTree(root->left); // 左
swap(root->left, root->right); // 中
invertTree(root->left); // 右
return root;
}
};(3)总结:
1.上来第二层的左右翻转,是带着下方的整体,不是只翻转7和2
2.中序遍历自己画图领会一下变的过程
101.对称二叉树
(1)题目描述:

(2)解题思路:
class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return false;
else if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return false;
else if (left == NULL && right == NULL) return true;
else if (left->val != right->val) return false;
else return compare(left->left, right->right) && compare(left->right, right->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
return compare(root->left, root->right);
}
};(3)总结:
1.主要是判断二叉树是否轴对称
2.注:最后的else是继续判断外侧和内侧,中间为且的关系只有两边都为true时才返回true
3.没看懂的话先看一下分开写的内外侧
class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
// 首先排除空节点的情况
if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return false;
else if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return false;
else if (left == NULL && right == NULL) return true;
// 排除了空节点,再排除数值不相同的情况
else if (left->val != right->val) return false;
// 此时就是:左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况
// 此时才做递归,做下一层的判断
bool outside = compare(left->left, right->right); // 左子树:左、 右子树:右
bool inside = compare(left->right, right->left); // 左子树:右、 右子树:左
bool isSame = outside && inside; // 左子树:中、 右子树:中 (逻辑处理)
return isSame;
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
return compare(root->left, root->right);
}
};104.二叉树的最大深度 (优先掌握递归)
(1)题目描述:

(2)解题思路:
class Solution {
public:
int getdepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中
return depth;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getdepth(root);
}
};(3)总结:
1.深度是节点到根节点的距离,高度是节点到叶子节点的距离

2.求高度要用后序遍历(左右中)把中间的处理过程返回给父节点,父节点就知道要加一,此时就实现了1、2、3从底往上的计数过程
3.求深度用前序遍历(中左右)往下遍历一个就加一
4.注:根节点的高度就是这棵树的最大深度
111.二叉树的最小深度 (优先掌握递归)
(1)题目描述:

(2)解题思路:
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右
// 中
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL) {
return 1 + rightDepth;
}
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL) {
return 1 + leftDepth;
}
int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return result;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root);
}
};